Executive summary: why invest in healthcare application development in 2025–2026?
The global digital health market exceeded $170 billion in 2024 and is projected to surpass $800 billion by 2030, according to industry analysts. This isn’t speculative growth—it’s the result of fundamental shifts in how care is delivered, paid for, and experienced. Post-COVID normalization of telehealth has moved virtual visits from emergency workaround to standard care option, with the WHO reporting that 76% of countries now have national digital health strategies in place.
At WTT Solutions, we approach healthcare application development differently. As a development company, we provide end-to-end healthcare application development services, ensuring regulatory compliance, security, and long-term support. Rather than treating it as a technology exercise, we focus on solving specific clinical, operational, and reimbursement pain points for healthcare organizations and startups. Our B2B and enterprise clients come to us not because they want “an app,” but because they need measurable outcomes: lower no-show rates by 20–30%, reduced administrative overhead by 25–40%, higher patient retention, and faster clinical decision-making through integrated data.
This guide is designed as a practical business resource. We’ll cover the current market landscape, the types of healthcare apps driving value today, must-have and next-generation features, a detailed development process, realistic costs and timelines, compliance essentials, and what to look for in a development partner. Whether you’re a startup founder validating a healthcare app idea or a health system CIO planning digital transformation, you’ll find actionable insights and innovative solutions that drive measurable outcomes throughout.

Healthcare app development market overview
The healthcare industry underwent a decade of digital transformation in just two years. When COVID-19 hit in 2020, telehealth visits for Medicare beneficiaries jumped from 0.1% to over 30% almost overnight. By 2023–2024, usage stabilized at sustainable levels, with telemedicine apps becoming permanent fixtures in most health systems’ service offerings. Remote patient monitoring, AI-driven diagnostics, and chronic disease management apps have followed similar adoption curves.
The numbers tell a compelling story. The global mHealth market is projected to reach $250 billion by 2026, growing at a 25% CAGR from 2021. Over 80% of US consumers now use some form of health app, and connected medical devices—from smart glucose monitors to wearable ECG patches—number in the hundreds of millions globally. This isn’t a bubble; it’s infrastructure being built. The rise of mobile health app development and mobile healthcare application development is a key driver of this digital transformation, enabling secure, interoperable, and innovative healthcare solutions.
Regulatory incentives are accelerating adoption. In the US, CMS has made many pandemic-era telehealth billing codes permanent, and Remote Therapeutic Monitoring (RTM) now has its own reimbursement pathway. In the EU, Germany’s DiGA framework allows physicians to prescribe certified digital health apps with statutory health insurance coverage. These policy changes create real revenue streams for healthcare mobile applications.
Three stakeholder groups drive demand for custom healthcare software development:
– Providers (hospitals, clinics, IDNs): Need patient access tools, care coordination platforms, operational dashboards, and hospital mobile app development to improve hospital management and resource allocation, all integrated with existing healthcare systems
– Payers (insurers, employer health plans): Seek member engagement apps, utilization management tools, and population health analytics
– Digital health startups: Require MVPs that can demonstrate clinical value, attract funding, and scale to meet enterprise requirements
At WTT Solutions, we see consistent macro-trends across our healthcare projects:
– Shift from stand-alone apps to integrated platforms that span multiple care settings
– Demand for interoperability via FHIR and HL7 standards, not proprietary data silos
– Cloud migration with enterprise-grade security (AWS, Azure, GCP with BAA coverage)
– Secure data sharing across care teams, including non-employed specialists and community providers
Key types of healthcare applications
Most successful healthcare apps don’t try to do everything at once. The strongest roadmaps focus on one primary use case and user group for the MVP, then expand based on adoption and feedback. That said, understanding the full landscape helps you position your product and identify integration opportunities.
Here are the main categories of healthcare applications WTT Solutions builds:
– Telemedicine platforms: Video visits, asynchronous consultations, and specialist e-consults. Primary users are patients and clinicians. Core goal: expand access, reduce travel burden, increase throughput. Example: Teladoc. Medical app development is crucial here to ensure the medical app is compliant, user-friendly, and supports secure remote patient care.
– Appointment and patient access apps: Self-service scheduling, check-in, forms, and waitlist management. Primary users are patients and front-desk staff. Core goal: reduce no-shows and phone volume. Example: Zocdoc.
– Chronic disease management and RPM: Connected monitoring devices, symptom logging, care plan tracking, and coaching. Primary users are patients with chronic conditions and care managers. Core goal: reduce hospitalizations and ED visits. Example: Livongo. Building a robust medical app through expert medical app development is essential for effective chronic disease management and regulatory compliance.
– Medication management: Pill reminders, refill tracking, interaction warnings, and adherence analytics. Primary users are patients and pharmacists. Core goal: improve adherence and reduce adverse events. Example: Medisafe.
– Hospital and clinic operations tools: Staff scheduling, bed management, equipment tracking, and internal communication. Primary users are administrators and clinical leaders. Core goal: improve operational efficiency. Example: Qgenda. These tools must efficiently manage patient data and secure medical records to ensure privacy and compliance.
– Wellness and prevention: Fitness tracking, nutrition logging, sleep monitoring, and health risk assessments. Primary users are consumers and employers. Core goal: engage healthy populations and reduce long-term costs. Example: Noom.
– Women’s health: Fertility tracking, pregnancy monitoring, menopause support, and maternal care coordination. Primary users are women across reproductive life stages. Core goal: improve health outcomes for underserved populations. Example: Flo.
– Health education and decision support: Condition-specific information, treatment plan explanations, and shared decision-making tools. Primary users are patients and families. Core goal: enhance patient education and informed consent. Example: Healthwise.
WTT Solutions typically helps clients choose 1–2 categories for their MVP based on ROI potential, reimbursement pathways, and technical feasibility. Trying to build a “super app” from day one usually leads to delays, budget overruns, and unfocused user experiences.
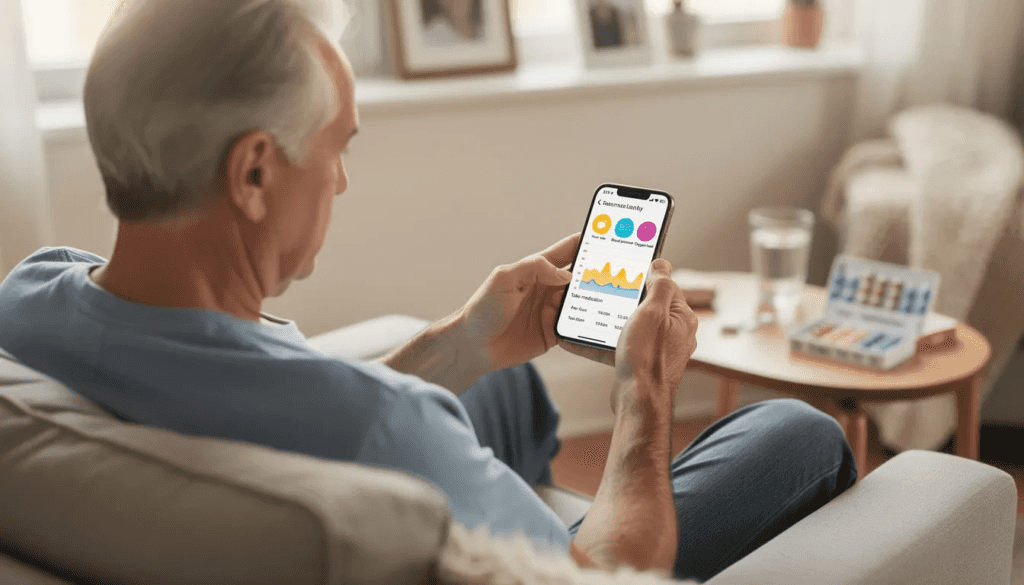
Patient-facing apps
Patient-facing healthcare apps live or die by usability, accessibility, and trust. These applications must work for an 80-year-old managing heart failure and a 30-year-old tracking fertility—often with vastly different technical literacy and device preferences.
Core features that drive ongoing patient engagement include:
– Symptom checkers and triage questionnaires
– Appointment booking with real-time availability
– Secure messaging with care teams
– Medication reminders and refill requests
– Integration with wearables for continuous data capture
– Seamless access to lab results, imaging reports, and visit summaries, ensuring patients can quickly and easily view vital medical information when they need it
Platform integrations are essential for consumer health apps. Apple HealthKit, Google Fit, and Samsung Health allow patients to share steps, heart rate, sleep data, and other metrics without manual entry. These integrations simplify onboarding and enable longitudinal health data collection that supports personalized care.
Mini use cases:
A diabetes companion app syncs CGM (continuous glucose monitor) data automatically, displays trends, and sends alerts when readings drift outside target ranges. Patients share weekly summaries with their endocrinologist through secure messaging.
A mental health app delivers CBT (cognitive behavioral therapy) modules, tracks mood over time, and offers asynchronous chat with a licensed therapist. Push notifications encourage daily check-ins without feeling intrusive.
A pregnancy tracking app provides week-by-week guidance, symptom logging, kick counting, and appointment reminders. It connects with the patient’s OB-GYN portal for seamless record sharing.
Accessibility and inclusive design are non-negotiables in regulated markets. WCAG 2.1 AA compliance, large font options for older users, high-contrast modes, and support for multiple languages aren’t nice-to-haves—they determine whether your app can serve the populations who need it most.
Clinician and admin-facing apps
Healthcare professionals need tools that fit into their workflows, not apps that create extra steps. The best clinician-facing applications reduce documentation burden, surface relevant information at the point of care, and enable seamless communication across care teams.
Common use cases include:
– Mobile EHR companions: Chart review, quick documentation, order entry, and results review from any location
– ePrescribing (eRx): Medication selection, dosing, electronic transmission to pharmacies, and prior authorization tracking
– Triage and clinical decision support: Risk scores, protocol checklists, and evidence-based guidelines
– Care coordination dashboards: Shared task lists, care gap alerts, and patient panel overviews
– Scheduling and staffing tools: Shift management, coverage requests, and capacity planning
These applications must integrate seamlessly with EHR/EMR systems like Epic, Cerner, Allscripts, and MEDITECH. FHIR and HL7 interfaces enable bidirectional data flow—pulling patient context into the app and pushing documentation back to the source system. Without solid integration, clinicians face duplicate data entry and fragmented workflows.
Admin-focused features support healthcare organizations at the operational level:
– Analytics on patient throughput and wait times
– Utilization reports for diagnostic equipment and procedure rooms
– Denial management dashboards tracking claim rejections by reason code
– Automated eligibility checks before appointments
WTT Solutions typically designs these applications as web or tablet-optimized solutions first, then selectively adds mobile where it genuinely improves workflows. Home health nurses checking in on patients benefit from mobile apps; hospitalists at workstations usually don’t need native phone apps.
Business benefits of custom healthcare application development
Healthcare application development should be justified with measurable business and clinical outcomes, not just “digital presence.” The organizations seeing real ROI are those who tie their apps to specific metrics: cost reduction, revenue generation, quality improvement, or patient satisfaction gains. Digital healthcare applications also enable organizations to expand healthcare services and improve accessibility, making care more available to a wider population.
Benefits flow to three groups: healthcare organizations, clinicians, and patients. Let’s break down what each can expect.
Benefits for healthcare organizations and startups
Well-designed healthcare apps reduce cost per encounter by automating intake, eligibility checks, and documentation. Based on industry benchmarks, organizations typically see 10–25% savings in administrative costs when replacing phone-based scheduling and paper forms with digital workflows.
No-show rates drop significantly with automated reminders and self-service rescheduling. A typical outpatient clinic with 18–20% no-show rates can reduce that to 8–10% using SMS and push notification reminders, waitlist automation, and pre-visit triage that confirms patient intent.
Revenue and growth opportunities multiply with digital capabilities:
– Subscription-based chronic care programs generate recurring revenue
– Employer partnerships for wellness and prevention services
– Telehealth offerings that serve patients beyond your local geography
– Value-based care contracts that reward outcomes you can now measure
Data becomes a strategic asset. Longitudinal datasets from app-generated interactions support outcomes research, quality improvement initiatives, and payer negotiations. You can demonstrate which interventions work and where resources should be allocated.
Example scenario: A mid-sized outpatient network in Texas implements a telehealth and scheduling suite built by WTT Solutions. Within 12 months, they reduce front-desk call volume by 35%, cut no-shows by 40%, and launch a remote monitoring program for their diabetic population that qualifies for CMS reimbursement.
Benefits for clinicians
Clinician burnout is a healthcare crisis in itself. Medical professionals spend nearly half their time on documentation and administrative tasks rather than patient care. Smart applications address this directly.
Mobile and web apps shorten documentation time per visit through:
– Templated notes with smart defaults
– Voice dictation with clinical vocabulary support
– Pre-populated fields from previous visits and external data sources
– Click-to-complete order sets for common scenarios
Unified task lists, secure chat, and shared care plans reduce miscommunication between doctors, nurses, and allied professionals across shifts and locations. When the night nurse can see exactly what the day team planned—and flag concerns in real-time—care coordination improves.
Risk reduction comes from automated alerts:
– Drug interaction warnings at the point of prescribing
– Allergy conflict notifications
– Gaps in care alerts (overdue labs, missed screenings)
– Abnormal result escalatio
A day in the life: Consider a hospitalist using a modern clinical app versus legacy systems. With legacy: log into three systems, search for patient charts, transcribe notes by hand, page specialists through an operator. With a well-designed app: single sign-on, patient context pulled automatically, voice-to-text documentation, one-tap specialist consults through secure messaging. That’s 30–45 minutes saved per shift—time that goes back to patients.
WTT Solutions emphasizes co-design with clinicians during discovery and usability testing. When medical professionals help shape the tool, adoption rates climb and “shadow IT” workarounds disappear.
Benefits for patients and families
Patients gain transparency and control over their healthcare experience. Access to visit summaries, lab results, and imaging reports—often within hours rather than days—supports shared decision-making and health literacy. When patients understand their conditions and treatment plans, adherence improves.
Family and caregiver access matters enormously for managing dependents:
– Proxy accounts for parents managing children’s care
– Multi-profile dashboards for caregivers supporting elderly parents
– Shared medication calendars across household members
– Care team messaging that includes family members when appropriate
Remote patient monitoring programs deliver measurable outcomes improvements. Connected blood pressure cuffs, glucometers, and weight scales paired with coaching and alerts help patients manage chronic conditions at home. Evidence consistently shows that RPM programs reduce hospitalizations and ED visits for conditions like heart failure and COPD.
Patient story: A 67-year-old patient with heart failure uses a connected weight scale and symptom-tracking app. When his weight increases by 4 pounds over two days—an early sign of fluid retention—the app alerts his care team. A nurse calls to adjust his diuretic dose, and an emergency admission is avoided.
Patient trust hinges on both usability and visible privacy and security cues. Clear consent flows, easy data export, transparent privacy policies, and obvious security indicators (like biometric login) reassure users that their sensitive patient data is protected.
Must-have features for modern healthcare applications
The exact feature set depends on your app type and target audience, but a core set appears in most successful healthcare applications. These features address security, operations, and clinical communication—the baseline components that healthcare providers and patients expect. Data security and regulatory compliance are foundational requirements for all modern healthcare applications, ensuring that sensitive patient information is protected and that the app meets industry standards such as HIPAA.
WTT Solutions recommends starting with a lean but solid feature set for MVP. Every feature adds complexity, cost, and maintenance burden. Build what you need to prove value, then expand based on real usage analytics and user feedback.
Here are the essential feature categories:
|
|
| Security & Authentication | MFA, SSO, RBAC, audit logs, encryption |
|---|
| Patient Journey | Onboarding, profiles, scheduling, reminders |
|---|
| Communication | Secure messaging, video visits, care team chat |
|---|
| Clinical | Medication management, care plans, documentation |
|---|
| Financial | Payments, billing, insurance verification |
|---|
Security, authentication, and access control
Healthcare apps handle protected health information, making security non-negotiable. Authentication requirements include:
– Email/phone verification during registration
– Strong password policies (length, complexity, history)
– Multi-factor authentication: SMS codes, authenticator apps (Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator), and biometrics (Face ID, Touch ID) on iOS and Android
Role-based access control ensures clinicians, administrators, and patients see only appropriate data. A front-desk scheduler shouldn’t access clinical notes; a patient shouldn’t see another patient’s records. For complex organizations, attribute-based access control (ABAC) adds granularity based on department, location, or care relationship.
Audit logs track every access, modification, and export of patient records. Session management enforces timeouts, device limits, and revocation capabilities. These aren’t optional for HIPAA or GDPR compliance—they’re essential for forensic analysis after any incident.
All patient data must be encrypted in transit using TLS 1.2 or higher. Data at rest requires field-level encryption or encrypted storage volumes. Reference NIST guidelines (SP 800-175B) for cryptographic standards.
WTT Solutions integrates with enterprise identity providers (Azure AD, Okta, Ping Identity) for large healthcare clients who need single sign-on across their application portfolio.
Core patient journey: onboarding, profiles, and scheduling
Patient onboarding must be simple with clear consent steps. Low-friction flows include:
– Email or phone number registration with verification
– Optional social logins (Apple, Google) for consumer apps where appropriate
– Progressive profile completion rather than long upfront forms
– Explicit consent for data collection, sharing, and communications
Patient and clinician profiles structure the data model:
|
|
| Patient | Demographics, conditions, medications, allergies, insurance, emergency contacts, communication preferences |
|---|
| Clinician | Name, credentials, specialties, languages spoken, locations, availability, bio |
|---|
Appointment scheduling capabilities should include:
– Search by specialty, location, and availability
– Real-time slot visibility with conflict prevention
– Waitlist management for cancellations
– Self-service rescheduling and cancellation
– Calendar sync (Google Calendar, Outlook, Apple Calendar)
Automated reminders via push notifications, SMS, and email reduce no-shows. Configurable notification rules let clinics customize reminder timing and frequency based on their policies.
For B2B applications, integration with existing practice management systems (Athenahealth, eClinicalWorks, NextGen) is essential to avoid double-booking and manual reconciliation.
Telemedicine and communication
Core telehealth capabilities form the backbone of many healthcare mobile applications:
– HD video visits with screen sharing and document upload
– Secure text chat between patients and providers
– Photo and file sharing for wound checks, rashes, and documents
– Asynchronous visits: store-and-forward questionnaires and pre-visit triage forms
Video infrastructure must be HIPAA-compliant. WebRTC with end-to-end encryption where possible, hosted by BAA-compliant vendors (Twilio, Vonage, Zoom Healthcare). Fallback options for low bandwidth—audio-only or phone dial-in—ensure visits don’t fail in rural areas.
In-app messaging reduces call center load and improves responsiveness. Group messaging among care teams supports handoffs and coordination. Patient-to-provider messaging handles routine questions without scheduling full appointments.
Telehealth integration with EHRs and billing systems is critical for reimbursement. Visit notes must flow back to electronic health records automatically. Billing integration applies appropriate CPT/ICD-10 codes and telehealth modifiers.
WTT Solutions has experience both building custom video modules and integrating third-party telehealth SDKs. Custom builds offer maximum flexibility; SDK integrations accelerate time-to-market. The right choice depends on your requirements and budget.
Medication, prescription, and care plan management
Medication management features support adherence and safety:
– Comprehensive medication lists with dosing schedules
– Refill reminders and one-tap refill requests
– Drug interaction warnings pulled from clinical databases
– Pill-taking checklists with confirmation tracking
ePrescription workflows (where legally permitted) streamline the prescribing process:
– Provider selects medication and dosage
– Electronic transmission to patient’s preferred pharmacy
– Tracking of fill status and prior authorization requirements
– Notifications when prescriptions are ready for pickup
– Integration with national drug databases (RxNorm in the US, SNOMED CT internationally) ensures consistent medication coding. Pharmacy network integrations (Surescripts in the US) enable electronic routing.
Broader care plan management helps patients navigate treatment plans:
– Goals with measurable targets
– Tasks and milestones with due dates
– Educational materials linked to specific conditions or procedures
– Follow-up scheduling tied to care plan progress
Visual presentation matters. Timelines, progress bars, and streak indicators improve adherence. WTT Solutions prioritizes UX for these features because the best clinical logic means nothing if patients don’t engage with it
Payments, billing, and insurance
In-app payment flows must balance convenience with compliance:
– Card payments (credit, debit, HSA/FSA cards)
– Digital wallets: Apple Pay, Google Pay
– Integration with payment service providers that support healthcare-specific requirements and recurring billing
Multiple billing models may apply depending on your business:
|
|
| Pay-per-visit | Traditional copay or self-pay consultations |
|---|
| Subscription | Chronic care programs, concierge medicine |
|---|
| Bundled pricing | Surgical episodes, care packages |
|---|
| Direct-to-employer | Workplace wellness programs |
|---|
Eligibility checks and insurance verification via clearinghouse APIs (Availity, Change Healthcare) reduce claim denials. Verifying coverage before the appointment prevents surprises for both patients and providers.
Price transparency is increasingly required by regulation. Displaying cost estimates before visits—including expected copays and deductibles—builds trust and reduces billing disputes.
B2B enterprise solutions often integrate directly with existing revenue cycle management and billing platforms rather than handling all payment logic within the app.
Next-generation features and technologies in healthcare apps
Organizations now look beyond basic telehealth toward AI, IoT, and advanced analytics. But next-generation features should be prioritized based on clear ROI and regulatory viability—not technology hype. A flashy AI feature that can’t be validated or reimbursed doesn’t help your business.
Here are the advanced capabilities WTT Solutions helps clients evaluate and implement:
AI and machine learning
AI delivers value across clinical and operational use cases:
– Symptom triage bots: Guide patients to appropriate care levels, reducing unnecessary ED visits
– Personalized care paths: Tailor education and interventions based on patient characteristics and behavior patterns
– Predictive models: Identify patients at high risk for readmission, falls, or deterioration
– Anomaly detection: Flag concerning trends in vital signs from remote monitoring data
Model selection depends on the use case. Gradient boosting works well for tabular risk scores. Deep learning powers medical imaging analysis—diabetic retinopathy screening now achieves 95% accuracy in research settings. NLP extracts structured data from clinical notes.
Explainability matters in regulated settings. Clinicians and regulators need to understand why an algorithm made a recommendation. Black-box models face adoption resistance and regulatory scrutiny.
Data requirements include high-quality labeled datasets, de-identification workflows for training data, and continuous monitoring for bias and model drift. An algorithm trained on one population may perform poorly on another.
AI also optimizes operations: demand forecasting for staffing, appointment slot optimization based on historical patterns, and automated coding suggestions that accelerate billing.
Compliance alignment is essential. When algorithms influence clinical decisions, FDA SaMD guidance may apply. Documentation for auditors should explain model development, validation, and monitoring processes.
IoT, wearables, and remote patient monitoring (RPM)
Connected devices transform chronic disease management. Common device categories include:
– Bluetooth blood pressure monitors
– Glucometers (finger-stick and CGM)
– Pulse oximeters
– ECG patches for arrhythmia detection
– Smart inhalers tracking medication usage
– Consumer wearables: Apple Watch, Fitbit, Garmin
Data ingestion flows typically involve:
– Mobile SDKs handling Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) connectivity
– Vendor APIs for cloud-connected devices
– Cloud IoT platforms (AWS IoT, Azure IoT Hub) for data aggregation and processing
Core RPM features for clinical teams:
– Real-time dashboards showing patient panels with vital sign trends
– Configurable alert thresholds (e.g., BP > 160/100, weight gain > 3 lbs in 2 days)
– Escalation rules routing alerts to appropriate team members
– Integration with care pathways and documentation
Reimbursement makes RPM financially viable. US CPT codes for Remote Patient Monitoring (99453, 99454, 99457, 99458) and Remote Therapeutic Monitoring (98975, 98976, 98977) create sustainable revenue streams.
RPM example: A hypertension management program equips patients with connected blood pressure cuffs. Patients take morning and evening readings at home. The app displays trends and provides coaching on lifestyle modifications. When readings exceed thresholds, care coordinators receive alerts and conduct outreach. Monthly reports support billing for RPM services.

Big data, analytics, and population health
Healthcare apps generate longitudinal data that can be aggregated for analysis. Data lakes and warehouses on AWS, Azure, or GCP store structured and unstructured health data from multiple sources. Typical analytics outputs include:
– Cohort dashboards tracking patient populations by condition, risk level, or care program
– Quality metrics: preventive care rates, chronic disease control, readmission rates
– Protocol adherence: Are patients following care plans? Where do they drop off?
– Cost and utilization trends across clinics, regions, or payer contracts
Standards support data portability. FHIR Bulk Data Export enables population-level data extraction. BI tools (Tableau, Power BI, Looker) connect to healthcare data sources for visualization and reporting.
Population health management uses analytics to identify high-risk cohorts, monitor intervention effectiveness, and report to payers or regulators. Healthcare organizations can demonstrate value and negotiate better contracts with data-driven insights.
Privacy-preserving analytics techniques—de-identification, pseudonymization, differential privacy—enable research and improvement without exposing individual patient records. Role-based access to analytical datasets ensures compliance with privacy regulations.
AR/VR, digital therapeutics, and behavioral change
Emerging technologies expand what healthcare apps can deliver:
AR/VR use cases:
– Surgical rehearsal using 3D reconstructions from imaging data
– Patient education: visualizing joint anatomy before orthopedic surgery
– Gamified physical therapy exercises performed at home with real-time feedback
– Pain distraction during procedures or wound care
Digital therapeutics (DTx): Software delivering evidence-based interventions for specific conditions. Unlike general wellness apps, DTx products often seek regulatory approval and reimbursement. Pear Therapeutics’ reSET (for substance use disorder) and Akili Interactive’s EndeavorRx (for ADHD) demonstrate the model.
Behavior change techniques built into apps drive sustained engagement:
– Streaks and achievements that reward consistency
– Goal-setting with incremental difficulty
– Push notification strategies informed by behavioral science
– Personalized nudges based on user patterns, not just time-based reminders
WTT Solutions focuses on clinically credible, evidence-aligned design when building experiences that claim health benefits. This often means partnering with clinical experts who can validate intervention design and outcome measurement.
Compliance, privacy, and security in healthcare application development
be addressed from day one. When you develop a healthcare app, compliance, privacy, and security should be core design principles from the very beginning, guiding every step of the process. Organizations that treat compliance as an afterthought face costly rewrites, delayed launches, and enterprise deals that fall through during security reviews.
The stakes are real. Healthcare data breaches cost an average of $10.1 million per incident in 2024 according to IBM. HIPAA violations can reach $50,000 per incident, with maximum annual penalties in the millions. Beyond fines, breaches destroy patient trust and organizational reputation.
HIPAA, GDPR, and other healthcare regulations
HIPAA governs protected health information in the US:
– Privacy Rule: Limits use and disclosure of PHI; requires patient rights to access and amend records
– Security Rule: Mandates administrative, physical, and technical safeguards for electronic PHI
– Breach Notification Rule: Requires notification to individuals, HHS, and sometimes media after breaches
– Business Associate Agreements (BAA): Required contracts with vendors handling PHI on your behalf
An app handles PHI when it stores, processes, or transmits individually identifiable health information on behalf of a covered entity (provider, payer, clearinghouse) or their business associates.
GDPR applies to health data for EU residents:
– Data minimization: collect only what’s necessary
– Purpose limitation: use data only for stated purposes
– Data subject rights: access, rectification, erasure, portability
– Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIA) for high-risk processing
– Special category data rules for health information (explicit consent or other legal bases)
FDA SaMD (Software as a Medical Device) and EU MDR apply when apps perform medical device-like functions:
– Diagnosis, treatment recommendations, or therapy delivery
– Risk classification determines regulatory pathway (510(k), De Novo, PMA in the US)
– Quality management systems and documentation requirements
WTT Solutions collaborates with clients’ legal and compliance teams to translate regulatory requirements into concrete product and architecture decisions. Not all wellness apps need full HIPAA compliance—but any integration with provider systems or insurers typically changes the compliance profile.
Designing for privacy and security from the outset
Privacy-by-design principles guide our approach:
– Collect only necessary data (no “just in case” fields)
– Clear consent flows with granular options for what users share
– Strong default privacy settings that users can relax if they choose
– Easy data export and deletion to support data subject rights
Technical safeguards include:
|
|
| Encryption | TLS 1.3 in transit, AES-256 at rest, field-level encryption for sensitive fields |
|---|
| Key management | HSM-backed key storage, regular rotation, separate keys per environment |
|---|
| API security | Authentication tokens, rate limiting, input validation, OWASP best practices |
|---|
| Infrastructure | Hardened containers, minimal attack surface, network segmentation |
|---|
Organizational measures matter as much as technology:
– Access control policies limiting who can access what
– Least-privilege for developers and support staff
– Regular security training for all team members
– Background checks for personnel with PHI access
Monitoring and logging enable detection and response:
– Centralized logs (ELK stack, Azure Monitor, Splunk)
– Anomaly detection for unusual access patterns
– Retention policies that respect privacy laws (keep what’s needed, delete what isn’t)
WTT Solutions recommends periodic third-party security audits, especially for apps used by hospitals, insurers, or public entities. Penetration testing and vulnerability assessments should occur before launch and regularly thereafter.
Healthcare app development process with WTT Solutions
WTT Solutions is a healthcare app development company offering comprehensive healthcare application development services, including custom healthcare app development tailored to the specific needs of healthcare providers. We deliver healthcare applications through a full-cycle approach: from discovery through UI/UX design, development, testing, launch, and long-term support. Our process is tailored to healthcare’s unique requirements: stakeholder workshops with clinicians and admin staff, regulatory checkpoints throughout, and interoperability planning from the start.
Typical timelines:
|
|
| Focused MVP | 2–4 months |
|---|
| Full platform v1 | 4–6 months |
|---|
| Interprise multi-module system | 6+ months |
|---|
Our collaboration practices—agile sprints, regular demos, and transparent reporting—are particularly valuable for non-technical founders and healthcare leaders who need visibility into progress without micromanaging technical decisions.

Discovery and product strategy
Discovery phase activities:
– Stakeholder interviews with clinicians, administrators, patients, and payers
– Workflow mapping for current processes and pain points
– Competitor and benchmark analysis
-Regulatory assessment for target markets
– KPI definition: What does success look like?
WTT Solutions helps refine product vision into concrete user journeys and feature sets prioritized by business value and technical risk. We create:
– Product roadmap with phased milestones
– High-level architecture sketch
– Risk register identifying compliance, integration, and technical risks
– Budget and timeline estimates aligned with client constraints
Example: A startup comes to us unsure whether to focus their MVP on telehealth, chronic disease management, or medication adherence. Through discovery interviews with potential customers (employers and health plans), we learn that telehealth is commoditized but medication adherence with employer wellness integration is underserved. That insight shapes a differentiated MVP.
This phase is where decisions about target geographies (US vs. EU vs. multi-region) and corresponding compliance regimes get formalized.
UX/UI design and prototyping
Design activities include:
– User flows mapping each journey from start to completion
– Low-fidelity wireframes for rapid iteration
– High-fidelity clickable prototypes in Figma or Adobe XD
– Design system creation for consistent UI components
Usability testing with real clinicians and patients is essential. We conduct moderated sessions where users attempt real tasks, identify friction points, and suggest improvements. Designs iterate based on this feedback before development begins. Platform considerations:
– iOS Human Interface Guidelines and Android Material Design
– Responsive web design for tablet and desktop access
– Accessibility standards (WCAG 2.1 AA)
– Design systems for organizations with multiple products
Prototypes serve multiple purposes beyond design validation. They can pitch investors, gather stakeholder buy-in across departments, or run early user pilots without full backend implementation.
The cost benefit is significant: fixing usability issues at the design stage costs a fraction of post-launch fixes. A button in the wrong place caught during prototyping is a 10-minute fix; discovered after launch, it’s a sprint’s worth of work plus app store resubmission.
Architecture, development, and integrations
WTT Solutions selects technology stacks based on project requirements:
|
|
| Web Frontend | React, Angular, Vue.j |
|---|
| Mobile | React Native, Flutter, native iOS (Swift), native Android (Kotlin) |
|---|
| Backend | Node.js, .NET, Java, Python |
|---|
| Cloud | AWS, Azure, GCP |
|---|
| Database | PostgreSQL, MongoDB, FHIR servers (HAPI, Smile CDR) |
|---|
Architecture decisions balance multiple factors:
– Microservices vs. modular monolith: complexity, team size, scaling needs
– Fault tolerance: graceful degradation when dependencies fail
– Scalability: horizontal scaling for traffic spikes
– Observability: logging, tracing, and metrics from day one
Integration work often represents the majority of effort in healthcare apps:
– EHR/EMR integration via FHIR R4 and HL7 v2 interfaces
– Claims and billing systems (clearinghouses, RCM platforms)
– Identity providers (Azure AD, Okta)
– Device vendors and IoT platforms
– Analytics platforms and data warehouses
– Third-party telehealth or messaging SDKs
Secure DevOps practices:
– CI/CD pipelines with automated testing and security scanning
– Infrastructure-as-code (Terraform, CloudFormation)
– Environment separation: development, staging, production
– Test data that respects privacy (synthetic or de-identified)
Documentation is essential for long-term maintainability: API documentation, integration guides, and admin manuals for operations teams.
Quality assurance, validation, and security testing
Testing combines automated and manual approaches:
– Unit tests: Individual components work correctly
– Integration tests: Components work together
– End-to-end tests: Complete user journeys succeed
– Performance tests: System handles expected load
– Cross-device testing: iOS versions, Android versions, browsers
Test scenarios reflect real healthcare workflows, including edge cases:
– Poor connectivity and offline modes
– Partial data (missing insurance, incomplete records)
– Session timeouts and re-authentication
– Concurrent access by multiple users
Security testing steps:
– Static analysis (SAST) scanning code for vulnerabilities
– Dynamic analysis (DAST) testing running applications
– Penetration testing by certified professionals
– Remediation and re-testing before launch
For apps approaching SaMD territory, validation and traceability are especially important. Requirements link to test cases; test results link to requirements. This documentation supports regulatory submissions and audits. Test data must be anonymized or synthetic. WTT Solutions uses de-identification tools and synthetic data generators to avoid exposing real patient health records during testing
Launch, monitoring, and continuous improvement
Deployment options depend on your audience:
– Public app stores: App Store and Google Play for consumer apps
– Enterprise distribution: MDM/MAM platforms (VMware Workspace ONE, Microsoft Intune) for organization-deployed apps
– Web portals: Direct access for web applications without app store submission
Monitoring and observability setup:
– Uptime monitoring with alerting (PagerDuty, Opsgenie)
– Error tracking (Sentry, Bugsnag)
– Performance metrics (response times, API latencies)
– Usage analytics (Mixpanel, Amplitude, Google Analytics)
Post-launch iteration cycles:
– Collect user feedback through in-app surveys, support tickets, and reviews
– Analyze behavior with funnel analysis and cohort retention
– Prioritize improvements based on impact and effort
– Release updates in regular cycles
Evolution example: A telehealth MVP launches with video visits and basic scheduling. Over 18 months, it evolves into a broader virtual care platform: adding asynchronous messaging, remote monitoring integration, care management tools, and employer portal capabilities. Each release builds on usage data and client feedback.
How to choose a healthcare app development partner
Healthcare app development is high-stakes work. Applications handle sensitive patient data, integrate with critical clinical systems, and face regulatory scrutiny. The wrong partner can mean delayed launches, compliance violations, and failed enterprise deals. Selecting a development company with proven experience as a healthcare app development company is crucial to ensure regulatory compliance, robust security, and long-term support for your healthcare technology initiatives.
Look beyond glossy portfolios. Dig into how vendors handle:
– Failed projects and lessons learned
– Complex legacy integrations
– Regulatory audits and security assessments
– Staff turnover and knowledge continuity
|
|
| Healthcare domain experience | Projects in telemedicine, RPM, patient portals, clinical tools; understanding of clinical workflows |
|---|
| Technical depth | Full-stack capabilities, modern architecture, cloud expertise |
|---|
| Security & compliance | HIPAA/GDPR experience, secure SDLC, audit history |
|---|
| Interoperability | FHIR/HL7 integration experience, EHR vendor relationships |
|---|
| Communication | Responsive, transparent, structured project management |
|---|
| Post-launch support | Maintenance plans, SLAs, long-term partnership orientation |
|---|
| Cultural fit | Aligned values, collaborative approach, timezone compatibility |
|---|
Market research and analysis for healthcare applications
Thorough market research is the cornerstone of successful healthcare mobile app development. Before investing in custom healthcare app solutions, it’s essential to understand the needs, behaviors, and pain points of your target audience—whether they are patients, healthcare providers, or both. By conducting comprehensive market research, healthcare app developers can identify gaps in the current healthcare applications landscape, uncover emerging trends, and pinpoint opportunities for innovation, such as remote patient monitoring or telemedicine.
Analyzing the competitive environment helps you understand what features and user experiences are already available, and where your healthcare mobile app can offer unique value. This process involves studying existing healthcare apps, gathering feedback from patients and healthcare providers, and assessing regulatory requirements that may impact app development.
Market research also informs the design and functionality of your healthcare app. By understanding user preferences and workflow challenges, experienced healthcare app developers can create intuitive, accessible, and user-centric applications that enhance patient care and improve health outcomes. For example, insights from market research might reveal a need for better chronic disease management tools or highlight the importance of seamless communication between patients and healthcare professionals.
Ultimately, investing in thorough market research ensures that your healthcare application is not only innovative but also relevant and effective. It enables you to develop a custom healthcare app that addresses real-world needs, supports both patients and healthcare providers, and stands out in a competitive market—leading to higher adoption rates and better patient engagement.
Integration with medical devices in healthcare applications
Integrating medical devices with healthcare applications is transforming the healthcare industry by enabling real-time health data collection, remote patient monitoring, and more personalized patient care. When healthcare apps connect with devices such as blood pressure monitors, glucose meters, smartwatches, or advanced medical imaging equipment, both patients and healthcare professionals gain immediate access to vital health information. This connectivity supports timely interventions, more accurate treatment plans, and improved patient outcomes.
For healthcare organizations, seamless integration with medical devices streamlines administrative tasks and enhances operational efficiency. Healthcare app developers must ensure that these integrations comply with relevant healthcare regulations, such as HIPAA in the US, and adhere to industry standards like fast healthcare interoperability resources (FHIR) for secure and standardized data exchange with electronic health records (EHR) systems.
The development of custom healthcare software that interfaces with medical devices requires a deep understanding of healthcare systems, medical imaging workflows, and the complexities of treatment plans. By leveraging advanced technologies such as predictive analytics and artificial intelligence, healthcare applications can analyze health data from connected devices to identify trends, predict potential health issues, and deliver proactive care recommendations.
Integration with medical devices also boosts patient engagement by providing users with actionable insights, reminders, and alerts directly through their healthcare mobile app. This empowers patients to take a more active role in managing their health, while healthcare providers benefit from continuous monitoring and more comprehensive patient records.
In summary, the integration of medical devices with healthcare applications is a key driver of innovation in the healthcare industry. It enables healthcare professionals and organizations to deliver higher-quality care, improve patient satisfaction, and achieve better health outcomes through the use of advanced, interoperable, and secure healthcare solutions.
What makes WTT Solutions a strong choice for healthcare application development
WTT Solutions is a healthcare app development company with deep expertise in medical app development for a range of healthcare use cases. We bring focused experience in healthcare alongside deep expertise in related verticals (EdTech, HRTech, MarTech). We’ve delivered telemedicine platforms, patient portals, RPM dashboards, and internal clinical tools for clients ranging from funded startups to established provider organizations.
End-to-end capabilities:
– Product discovery and strategy
– UX/UI design
– Backend and frontend engineering
– iOS and Android mobile development
– EHR/EMR and third-party integrations
– AI/ML implementation
– Long-term maintenance and support
Compliance and security approach:
– Working under client compliance policies and legal guidance
– Alignment with HIPAA, GDPR, and relevant healthcare regulations
– Secure development practices with regular code reviews
– Third-party security audits available
– BAA execution with covered entities
Collaborative model:
– Agile delivery with 2-week sprints
– Regular demos and stakeholder reviews
– Transparent reporting via shared dashboards
– Dedicated product teams adaptable to your organization size
With offices in Dallas, Texas and Germany, WTT Solutions offers accessible collaboration for US and European clients—whether you need nearshore efficiency or occasional onsite presence.
Ready to explore your healthcare application idea?Get Started by scheduling a consultation to discuss your vision, timeline, and budget. We’ll help you understand what’s realistic and map a path to launch.